The concentration of indoor air pollutants can be up to five times higher than outdoors according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) of the United States. (source)
Therefore, this article highlights the importance of indoor air quality, common pollutants, and ways to prevent and mitigate the effects of poor air quality.
Common indoor air pollutants are carbon monoxide, VOCs, radon, CO2, fine dust, and mold. Potential health effects differ per pollutant and include irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat, headaches, nausea, and fatigue. Preventive measures include continuous ventilation, good cleaning habits, and installing an air quality monitor.
At the end of this article, you will find an overview table of all the common indoor air pollutants, their health effects, and preventive measures.
Why is indoor air quality important?
Good quality air contributes to your wellbeing and comfort as well as your productivity. However, when the air you breathe contains several hazardous compounds it can lead to a multitude of complaints and health effects, both in the short and long term.
The health effects of poor air quality
Normally health effects due to bad air quality will be minor such as dry eyes, a little fatigue, or a cough. However, some compounds can have more serious health effects.
Increased exposure, whether due to higher concentrations or longer exposure time, increases the potential health effects. Another important factor is your overall wellbeing, age, and possible sensitivity to the compound.

The immediate effects of bad indoor air
Sometimes exposure to air pollutants can lead to immediate health effects. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), these effects can be:
- irritation of the eyes, nose, or throat
- headaches
- dizziness
- fatigue
- increased symptoms of asthma or any other illness
Long-term health effects
The EPA states that long-term health effects of indoor air pollutants may show up years after exposure or after long or repeated periods of exposure. Possible long-term adverse health effects include:
- respiratory disease
- heart disease
- cancer
On top of that, repeated exposure to hazardous substances can cause sensitization.
Young children are most at risk
Children are more susceptible to indoor air pollutants because they inhale more air and thus pollutants per kg of body weight than adults. Additionally, children’s airways are narrower than adults, so irritation and swelling of the airways can result in relatively greater airway blockage.
Taking immediate action
The short-term health effects can easily be overlooked and will often not be contributed to poor air quality. And even if you identify that your cough or fatigue might be caused by air pollution, you do not always know the source.
What you can do immediately when you notice health effects that may be caused by air pollutants is to open doors and windows to air the room. If you have an indication of the source of the pollutants, removing the source or removing yourself from the source should eliminate the problem.
Of course, it is best to prevent the health effects of bad indoor air quality by taking measures beforehand. So, when you suspect some health effects could be caused by long-term exposure, it is wise to take serious measures.
Appliances and household products of concern
There are several common sources of indoor air pollutants that are present in almost every home or office. These appliances and products should be used with care and maintained properly in order to minimize their contribution to poor indoor air.
These products and appliances include:
- cleaning products
- carpets
- poorly cleaned or maintained ventilation
- geysers, boilers, and central heating system
- gas stove and fireplace
- paint
- candles and incense
Cleaning products
Surprisingly, cleaning agents are a source of air pollution. Exposure to compounds emitted from cleaning agents depends on many factors, including its composition and reactive chemistry. It is safest to use natural cleaning agents.

Carpets and rugs
The relationship between carpets and rugs and indoor air quality is an interesting one. Carpets and rugs trap dust particles that are kicked back into the air when you walk over them. Hereby, they contribute to a continuous circulation of airborne dust.
However, since carpets and rugs trap dust particles, they can be a dust sink when vacuumed regularly. Hereby, they can potentially contribute to the removal of airborne dust.
Additionally, carpets and rugs can themselves be a source of hazardous compounds since they wear out every time you walk on them.
If you are considering purchasing a rug, or already have a carpet or rug and want to replace it, I recommend considering buying a natural rug that does not contain hazardous substances.
Poorly cleaned or maintained ventilation
Ventilation is the most important factor for indoor air quality. Proper ventilation makes sure stale and polluted indoor air is transported outside and fresh outdoor air enters the room.
Is it strongly recommended to make sure you ventilate constantly and sufficiently. Therefore, you need to make sure that your ventilation system is regularly maintained and cleaned.
A general rule for the ventilation system is to clean it every three months and replace the filters twice a year. This, of course, depends highly on for example if you have pets or allergies (in that case you should replace and clean more often).
Geysers, boilers and central heating system
Household heating systems are a source of concern mostly due to their emission of carbon monoxide (CO). CO is emitted even from the most efficient appliances. Therefore, it is recommended to hang a few carbon monoxide detectors in your house. Most commonly in the bedroom to protect you while you sleep. Depending on where the water heating system is situated, another CO detector should be installed.
Gas stove and fireplace
The gas stove and fireplace are both sources of carbon monoxide as well as fine dust particles. Proper ventilation and airing when using the fireplace or when you are cooking is highly recommended. Installing a carbon monoxide detector is another safety precaution.
Candles and incense
Candles and incense can, unfortunately, consist of and therefore emit all kinds of potentially harmful compounds. A common air pollutant coming from candles is particulate matter or fine dust. These are very small particles that can enter your lungs and damage them. Inhaling these particles is similar to (secondhand) smoking.
Healthier options are vegetable-based candles, soy candles, or beeswax candles.
Paint
Regular paint is a source of air pollutants called volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These compounds are emitted from paint during the drying process, therefore it is recommended to air and ventilate constantly during painting. Additionally, according to an extensive study on the release of VOCs during and after painting, it is recommended to at least not use the painted room for 14 days. Another option is to look for low-VOC paint.
Do plants improve indoor air quality?
In short, yes, houseplants do help improve indoor air quality. However, there seem to be many blog posts on the internet claiming that NASA published a list of the best houseplants to purify your indoor air.
The truth is that proper ventilation is by far the most important for indoor air quality. Plants should never be a substitute for good habits such as ventilation and regular cleaning. I wrote an article on the topic of houseplants that you can read here.
Good habits to prevent exposure to indoor air pollutants
There are several good habits that you can adopt to make sure your exposure to air pollutants is minimized.
Continuously ventilate
Good ventilation is key for good air quality in every room of your apartment. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), indoor air quality is normally about five times worse than outdoor air. Therefore, ventilation should be happening constantly to provide fresh air and remove stale, polluted indoor air.
Good ventilation means that you make sure there is constant air exchange between the outside air and the indoor air. This can be achieved by making sure all your ventilation vents are always open. Additionally, regularly opening a window to air out the house is recommended.
Ventilation and heating
One issue with constant ventilation, however, is that air exchange often means heat loss (or gain, depending on your local climate). If you are interested in learning about heat-recovery ventilation systems, you can read our article: Heat-recovery ventilation in a well-insulated house.
However, in your apartment, you will likely not have the option to change your ventilation system. You could consider contacting your landlord on this issue, and see if they are willing to invest in a better ventilation system.
Always turn on the extractor hood in the kitchen
Cooking is a source of air pollution, therefore, you should make sure to always turn on the hood. Run it on the highest option you are comfortable with.
Additionally, whenever you are not using all the stove burners, try to use the ones that are best vented by the extractor hood. These are usually the ones at the back. Also, make sure the extractor hood is always clean and in good condition.
Vacuum regularly
By vacuuming often, you will remove fine dust particles that will otherwise become airborne. Fine dust particles easily enter the lungs and may cause long-term health effects.
Don’t skip a good cleaning session
To prevent mold growth, especially in the bathroom, proper cleaning is required. It is easy to do a general cleaning session and skip the important parts such as the grout lines between your bathroom tiles. However, in this way you allow mold growth to build up, making them harder to remove the next time. I would recommend wiping the grout lines with regularity.
Additionally, you should consider drying the shower walls and tiles after you have taken a shower, This again prevents the potential for mold growth. On top of that, the showerhead and faucets heads require a good clean as well.
Common indoor air pollutants
There are many compounds that reduce air quality and pose some kind of health risk. The health risk is dependent on several factors. These include the type of compound, the amount present in your air, your exposure to them, and your overall health.
The most common air pollutants found indoors are:
- fine dust particles
- carbon monoxide (CO)
- CO2 (carbon dioxide)
- radon gas
- volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
- formaldehyde
- mold
Unfortunately, most air pollutants are not noticeable since they are odorless and colorless. Therefore, it is wise to get to know how these compounds enter your air. What their potential health effects are, and most importantly, how to take preventive measures.
Fine dust
Fine dust particles are really small dust particles. They are especially harmful since they can more easily enter your lungs compared to regular dust. Fine dust is found all over the house.
Indoor fine dust has many causes, including cooking, lighting candles, and outdoor air (coming from car exhausts). Unfortunately, there are no safe levels of fine dust.
Health effects of fine dust
Inhaling fine dust particles can lead to several health issues such as:
- irritation of airways
- decreased lung function
- an increase in respiratory problems and asthma
- premature death in people with lung or heart disease
How to prevent fine dust?
Fine dust particles can best be prevented by regularly vacuuming the house and making sure your ventilation is working properly. Be sure to continuously ventilate and regularly clean or replace the ventilation vents. Also, don’t forget to change your vacuum cleaner bag.
CO2 (carbon dioxide)
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an odorless, colorless gas that only causes health issues in relatively high concentrations. You can read all about CO2 in our article: What are healthy indoor CO2 levels?
Carbon monoxide (CO)
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless odorless gas that is formed by the incomplete burning of carbon-based fuels. Incomplete burning happens in all fires but also in (efficient) appliances.
The most common sources of carbon monoxide are central heating systems and kerosene and gas space heaters such as geysers and boilers. Other sources of CO are gas stoves and the fireplace. Additionally, CO can enter the house via leaking chimneys and vents. Tobacco smoke is another source of carbon monoxide.
Health effects of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide, when inhaled, quickly enters the bloodstream and reduces the blood’s ability to carry oxygen. This results in oxygen deprivation which can be deadly in high doses and causes all kinds of health effects. The following figure shows the health effects of CO exposure related to an increase of CO exposure. (source: World Health Organisation)
Keep in mind that health effects depend on many factors such as level of exposure, duration of exposure, and the overall health of the person exposed.
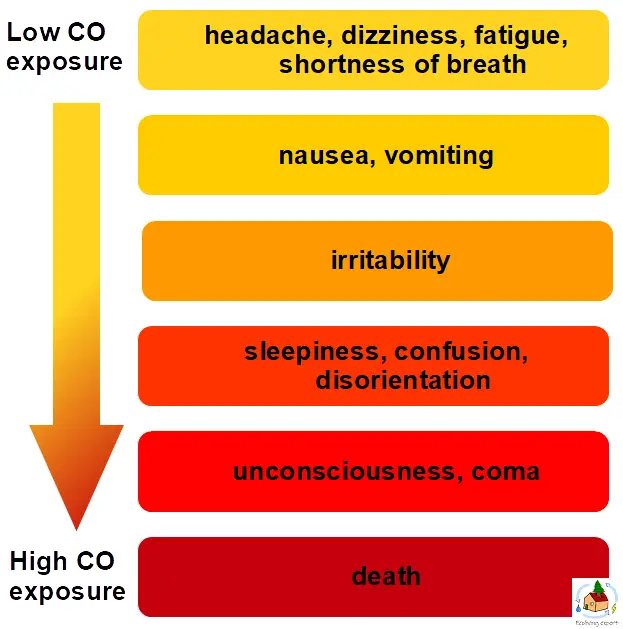
How to prevent carbon monoxide exposure
Exposure to carbon monoxide can be minimized by taking care of the following:
- install a carbon monoxide detector in every room (and replace the batteries every 6 months)
- proper installation, maintenance, and use of combustion appliances
- clean your fireplace and chimney once a year
- change your gas stove to an electric stove
- ventilate constantly
- clean ventilation vents regularly
Carbon monoxide detectors
To make sure you are safe from carbon monoxide, a CO detector is a must-have. Ideally, you place one near your boiler or geyser, and one in the bedroom to make sure you are safe during the night.
This article on safety.com shows the laws of every US state regarding CO detectors.
A carbon monoxide detector is cheap and you can simply order them on amazon via the picture below.
Radon gas
In the United States, radon gas is the second leading cause of lung cancer. Radon is prevalent in many parts of the world. You can read all about radon in our article: What is radon? (origin, health risk, and preventive measures).
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
Volatile organic compounds are mostly human-made chemicals that are emitted as a gas from solids or liquid. There are very many different VOCs and their effects can range from highly toxic to no known negative health effects. (source)
The most common sources of VOCs are:
- paint
- cleaning products
- deodorizers
- dry cleaning fluids
Health effects of VOC exposure
Acute health effects of VOC exposure include:
- headache, dizziness, loss of coordination, nausea, visual disorder
- irritation of eyes and respiratory tract
- allergic reactions including asthma and rhinitis
Chronic exposure to VOCs can lead to the following effects:
- damage to kidney, liver, blood system, and central nervous system
- some VOCs may cause cancer. (Formaldehyde)
How to prevent VOC exposure
Exposure to volatile organic compounds can be minimized by taking care of the following:
- never mix cleaning agents unless specified by the manufacturer
- make sure to provide enough fresh air when using cleaning agents
- use natural no-VOC cleaning agents
- use low VOC paints in your house
Formaldehyde
Technically formaldehyde is a common VOC. However, I want to mention it separately because it is stated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to potentially cause cancer. It is a colorless, pungent-smelling gas and can be released from insulation and building materials such as composite wood. Other sources are:
- cleaning products, fabric softeners and conditioners
- carpeting
- glues and resins
- tobacco smoke
- a type of insulation called urea-formaldehyde insulating foam (UFFI)
How to prevent formaldehyde exposure
Exposure to formaldehyde can be minimized by taking care of the following:
- use formaldehyde-free or natural cleaning products
- apply natural insulation and building materials
- use natural no-VOC carpeting and rugs (I recommend naturalarearugs.com)
Additionally, according to the EPA, the rate at which formaldehyde is released is increased by heat and may be affected by humidity. Therefore, maintaining moderate humidity and temperature levels can reduce exposure. The EPA advises air dehumidifiers to control indoor humidity. (source) You can read more about dehumidifiers and air quality monitors below.
Mold growth
The spores of molds are always present in the air in very small quantities. They normally do not pose any health hazards. However, when mold spores land in a spot that is humid and warm, they can start to grow and produce very high quantities of spores. This can lead to various health effects and can damage wood and fixtures.
The bathroom is the most common room with mold issues since they are often very wet and the air generally has a very high relative humidity.
Negative health effects of mold
Mold growth can cause several health problems, mostly due to inhalation of high quantities of spores or contact with the skin. Health effects include (source):
- irritation of eyes, nose, skin, lungs, and throat
- allergic reaction
- asthmatic problems
- respiratory ailments
Preventing mold growth and exposure
There are several ways to prevent mold growth and exposure to its spores.
- regular and thorough cleaning
- continuous ventilation
- installing an air dehumidifier
- wear gloves, goggles and a mask when mold growth is extensive
What you can do ensure clean indoor air
Aside from the already mentioned good habits and maintenance of your ventilation system, there are a few appliances that help improve air quality.
Air dehumidifiers
A dehumidifier is a device that takes up excess humidity from the air. They are mostly effective against mold growth and the release of VOCs. Additionally, it makes the indoors more comfortable.
There are many dehumidifiers in a wide price range and for many different areas such as the wardrobe, bedroom, or living room. I studied some of the available dehumidifiers and think that for a medium-sized apartment, a regular small-sized dehumidifier should do just fine. I would recommend taking a look at the options on Amazon, such as this one.
Air quality monitors
To make sure you are always aware of the levels of humidity, VOCs, and other harmful substances in your house, an air quality monitor is an excellent tool. An air quality monitor can measure airborne chemicals, temperature, and humidity, depending on the device.
If you are interested in buying an air quality monitor, I would recommend choosing a model that measures a wide range of air pollutants. In this way, you never have to worry if you are missing just that one compound that is causing problems.
Why I recommend using an air quality monitor instead
Although an air purifier is a wonderful tool, ventilation is still your best weapon against indoor air pollution. Therefore, measuring the air with a good air quality monitor and ventilating when necessary is an excellent alternative to an air purifier. An air quality monitor has the advantage over an air purifier in that it tests for more compounds than an air purifier can remove. For example, an air quality monitor informs you about the presence of carbon monoxide and radon. An air purifier does not, and can’t remove these compounds from the air.
In looking for the best air quality monitors available, I found a Norwegian company called Airthings, which produces exceptional air quality monitors. They are easy to operate (just wave your hand in front of the device) and send their data to an app on your phone.
Get a 10% discount on Airthings air quality monitors
Readers of this website can get a 10% discount on Airthings devices using my coupon code. With the following coupon code, you can access the discount store: discount.airthings.com. Here, you will get access and 10% off when entering this coupon code: 665381-10OFF.
Overview table
Table 1. Overview of common pollutants, their health effects, and preventive measures.
| Hazardous compounds | Sources | Health effects | Preventive measures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fine dust particles | – fuel-burning such as car exhaust and fire – cooking – lighting candles – smoke – natural causes | – irritation of airways – decreased lung function – an increase in respiratory problems and asthma – premature death in people with lung or heart disease | – ventilate constantly – improve ventilation system – consider natural carpet and vacuum it often – install an air quality monitor |
| Carbon monoxide (CO) | – incomplete burning of fuel – central heating system – fire(place) – leaky chimneys and vents | – depends on the amount of CO – ranges from fatigue to confusion to potential death | – install a carbon monoxide detector – clean your fireplace and chimney once a year |
| CO2 (carbon dioxide) | – car exhausts and (human) exhalation – improper ventilation | – depends on the amount of CO2 – bar air complaints, headache, sleepiness, loss of concentration | – ventilate constantly and properly – air out the house regularly – monitor air quality |
| Radon gas | – soil and groundwater | – causes lung cancer | – increase ventilation underneath the floor – install a radon sump system underneath the floor or in the basement – seal floors and walls – improve the ventilation of your house – install a radon ventilation fan |
| VOCs | – cleaning products – deodorizers – dry cleaning fluids – paint | – headache, dizziness, loss of coordination, – nausea, visual disorder – irritation of eyes and respiratory tract – allergic reactions | – use cleaning agents according to instructions – never mix cleaning agents – provide fresh air when cleaning – use natural no-VOC cleaning agents – use low VOC paints |
| Formaldehyde | – cleaning products, fabric softeners and conditioners – carpets – glues and resins – tobacco smoke – UFFI insulation | – headache, dizziness, loss of coordination, nausea, visual disorder – irritation of eyes and respiratory tract – allergic reactions – Formaldehyde potentially causes cancer | – use formaldehyde-free or natural cleaning products – apply natural insulation and building materials – consider natural no-VOC rugs |
| Mold | – spores in outdoor air | – irritation of eyes, nose, skin, lungs, and throat – allergic reaction – asthmatic problems – respiratory ailments | – regular and thorough cleaning – continuous ventilation – installing an air dehumidifier |




1 thought on “The complete indoor air quality guide for your home (with giant overview table)”
Comments are closed.